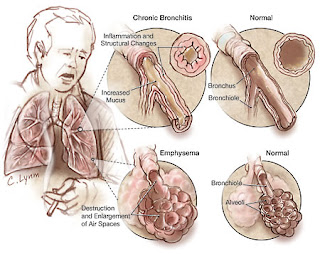
Chronic Bronchitis
Chronic bronchitis is a disease, characterized by cough with phlegm every day, at least 3 months per year and lasts for 2 consecutive years, and the absence of other diseases with symptoms.
Etiology and pathogenesis
Etiology
a. Cigarette smoke is a disincentive to the bronchial mucosa, to changes:
b. Exposure to air polluted by industrial pollution or the disposal of fuel combustion in motor vehicles:
Clinical Symtoms
Special examination of Chronic bronchitis
Management Of Chronic bronchitis
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of chronic bronchitis is based on:
Differential Diagnosis
Prognosis
Etiology and pathogenesis
Etiology
- Exposure to cigarette smoke, both at the "smoker" or "passive smoker". For the smoker is usually measured by pack year (pack years).
- Exposure to contaminated air in workplaces (eg dust or gas from industrial or workplace).
- Social factors and residential solid and air pollution in the settlement area by the gases SO2 and NO2.
- Respiratory tract infection by the virus will cause eksaserbrasi chronic bronchitis. For example, by class sinsisial respiratory viruses and influenza virus group.
- Most bacteria that are found in chronic bronchitis are streptococcus pneumonia and haemophilus influenza.
a. Cigarette smoke is a disincentive to the bronchial mucosa, to changes:
- Lung Defense:
- Purge function mukosilia slow,
- Alveoler Macrophage numbers are increasing,
- Impaired macrophage function,
- The process of antigen and antigen response to change.
- Small airways:
- Inflammation,
- The increased muscle,
- Fibrosis,
- Refinement,
- The number of goblet cells increases.
- Alveoli:
- The number of neutrophils, macrophages increased,
- Emphysema.
b. Exposure to air polluted by industrial pollution or the disposal of fuel combustion in motor vehicles:
- Sulfur dioxide (SO2) and the complex particles (<10 u), derived from: Fossil fuels, power generation, oil refining, tobacco smoke, kerosene heaters, stoves that use wood or coal fuel. These materials cause bronchoconstriction.
- Photochemical oxidants, nitrogen oxides, ozone, produced by burning fuel in motor vehicles, power plants, and solar radiation. These materials cause stimulation of the respiratory tract, impaired pulmonary physiology and impaired pulmonary defense.
- Carbon monoxide (CO) generated by the combustion of automotive fuel, cigarette smoke. CO causes tissue hypoxia, especially the cardiovascular and nervous systems.
Clinical Symtoms
- Chronic cough with phlegm mucus, thick, a lot, especially in the morning. Muko-purulent sputum, or purulent if there is infection. These symptoms for cough are considered regular smokers.
- Shortness of breath with breath sounds due to progressive inflammation and bronchial obstruction.
- If the disease has continued to grow, especially shortness of running time.
- Physical examination performed on the patient sitting position:
- Chest hyperinflation
- Percussion hipersonor
- wet crackles at the time of inspiration
- Wheezing on expiration time.
Special examination of Chronic bronchitis
Management Of Chronic bronchitis
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of chronic bronchitis is based on:
- Anamnesa according to the criteria of chronic bronchitis with symptoms of chronic cough and phlegm, especially in the early morning, thick sputum and numerous. Sometimes purulent, especially in heavy smokers. Shortness of breath during activity and occurs slowly but progressively.
- Physical examination is not typical, usually chest hyperinflation, hipersonor, wet crackles and sometimes audible wheezing.
- Chest X-ray photo showed lung hyperinflation with increased bronchovascular markings.
- Examination of sputum Gram to detect bacterial infection in exacerbation.
- Lung physiology tests to detect obstruction or restriction.
- ECG to determine heart abnormalities.
- Arteriel blood gas analysis to detect hypoxemia and hypercapnea.
Differential Diagnosis
- Bronchial Asthma
- Pulmonary Emphysema
- Bronchiectasis
- Lung Carcinoma
- Cystic fibrosis
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis.
- Exacerbation acute respiratory tract infections, pneumonia.
- Pulmonary Emphysema
- respiratory failure
- Cor pulmonale.
Prognosis
- Depending on the early treatment before the disorder is advanced lung physiology and the presence or absence of complications of emphysema and cor pulmonale.
- Stop smoking, avoid air pollution and socio-economic improvement of the patient will improve prognosis.


Comments
Post a Comment